
题目列表(包括答案和解析)
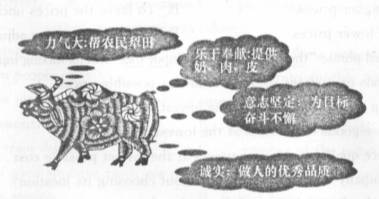
假如你是下面邮件的接收者,请你根据其内容并结合图画信息写封回信,同时祝对方牛年快乐。
注意:1.词数120左右,信的开头和结尾已为你写好(不计人总词数)。
2.可根据内容要点适当增加细节,使行文连贯。
3.参考词汇:犁田 plough the farmland 象征性的symbolic
<From:jessielove@hotmail.com> |
<To:liyongsichuanchina@gmail.com> |
<Subject: I’m puzzled> |
Dear Li Yong. How are you? I hear that 2009 is the year of the bull in the Chinese lunar calendar, I am so curious about this , You know that we New Zealanders keep millions of bulls throughout the coutry here, yet many of us don’t know much about the bull in the eyes of the Chinese people . What’s the symbolic significance of the bull? Would you please tell me something about it / Waiting for your reply Best wish ! Yours, Jessie |
<From: liyongsichuanchina@gmail.com> |
<To: jessielove@hotmail.com> |
<Subject: Happy 牛(Bull) Year> |
Dear Jssie. How are you doing these days? I ‘ve received your letter and now
|
阅读下列短文, 从所给的四个选项中, 选出一个最佳答案。
The cold afternoon sunlight made long shadows behind the trees along the road. Sam Higbee 1 the gate of the Higbee Place and 2 his tractor(拖拉机)into the field. Things had been moving 3 . Only the night before, the Higbee 4 had at last stopped quarrelling for long enough to agree on a 5 price. John Farnham,the real-estate agent(房地产代理商),had 6 a hurried trip to see Higbee the next morning. Within a few hours Higbee had looked round the place again, the agreement had been 7 , and he had put his horses into one of the Higbee fields. Now he was 8 to plough(犁地).
He'd work until midnight, or 9 if he didn't get too10 . Out in the center of the field the old house was 11 the big trees.A dusty road ran 12 the field to the house from the gate. 13 Higbee had no use for the big old house. The 14 would cost more than the place was 15 . He lowered the 16 and started the tractor. 17 he ploughed the rich black earth 18 out in smooth furrows(犁沟). Low dark clouds moved past overhead, and in the west the 19 sun turned the lower parts of the clouds red.The 20 of the tractor's motor was unchanging, and watching the furrows sent Sam into a dream-like 21 . He didn't notice the time 22 .When it got dark, he 23 the headlight and kept going. The 24 night air caused sharp pain to his face and hands, but his 25 remained fixed on the piece of ground between the grass and the ploughed earth.
| 1. | A. looked at | B. opened | C. pushed | D. knocked at | [ ] |
| 2. | A. drove | B. moved | C. carried | D. rode | [ ] |
| 3. | A. sometimes | B. carelessly | C. slowly | D. quickly | [ ] |
| 4. | A. house | B. home | C. family | D. place | [ ] |
| 5. | A. selling | B. buying | C. rising | D. different | [ ] |
| 6. | A. made | B. tried | C. planned | D. delayed | [ ] |
| 7. | A. missing | B. read | C. seen | D. singed | [ ] |
| 8. | A. stopping | B. starting | C. continuing | D. forced | [ ] |
| 9. | A. harder | B. shorter | C. longer | D. earlier | [ ] |
| 10. | A. sleepy | B. hungry | C. excited | D. sad | [ ] |
| 11. | A. between | B. among | C. in | D. under | [ ] |
| 12. | A. over | B. into | C. through | D. below | [ ] |
| 13. | A. Therefore | B. Or | C. And | D. But | [ ] |
| 14. | A. repairs | B. buildings | C. painting | D. checks | [ ] |
| 15. | A. useful | B. worth | C. sold | D. bought | [ ] |
| 16. | A. machine | B. wheels | C. head | D. plough | [ ] |
| 17. | A. For | B. Since | C. As | D. Because | [ ] |
| 18. | A. rolled | B. ran | C. walked | D. went | [ ] |
| 19. | A. shining | B. strong | C. setting | D. failed | [ ] |
| 20. | A. voice | B. sound | C. size | D. movement | [ ] |
| 21. | A. place | B. situation | C. form | D. state | [ ] |
| 22. | A. turning | B. moving | C. passing | D. disappearing | [ ] |
| 23. | A. turned on | B. turned off | C. opened | D. fixed | [ ] |
| 24. | A. warm | B. cold | C. hot | D. dirty | [ ] |
| 25. | A. thought | B. face | C. hands | D. eyes | [ ] |
In the earliest stages of man’s development he had no more need of money than animals have. He was content with very simple forms of shelter, made his own rough tools and weapons and could provide food and clothing for himself and his family from natural materials around him. As he became more civilized, however, he began to want better shelter, more efficient tools and weapons, and more comfortable and more lasting clothing than could be provided by his own neighborhood or by the work of his own unskilled hands. For these things he had to turn to the skilled people such as smiths, leather workers or carpenters. It was then that the question of payment arose.
At first he got what he wanted by a simple process of exchange. The smith who had not the time to look after land or cattle was glad to take meat or grain from the farmer in exchange for an axe or a plough (犁). But as more and more goods which had no fixed exchange value came on the market, exchange became too complicated to be satisfactory. Another problem arose when those who made things wanted to get stocks of wood or leather, or iron, but had nothing to offer in exchange until their finished goods were ready.
Thus the difficulties of exchange led by degree to the invention of money. In some countries easily handled things like seeds or shells were given a certain value and farmer, instead of paying the smith for a new axe by giving him some meat or grain, gave him so many shells. If the smith had any shells left when he had bought his food, he could get stocks of the raw materials of his trade. In some countries quite large things such as cows or camels or even big flat stones were used for trade. Later, pieces of metal, bearing values according to the rarity (稀有) of the metal and the size of the pieces, or coins were used. Money as we know it had arrived.
What does the first paragraph mainly tell us?
A. Man needed little in the earliest stages of development.
B. Man preferred to make tools by himself.
C. How the simple process of exchange arose.
D. What the early man needed from others.
As men became more civilized they __________.
A. all learnt to make by themselves the things needed
B. had to travel a lot to look for what they wanted
C. wanted better things than those they themselves could provide
D. no longer provided food and clothing for themselves
Exchange of goods became difficult because __________.
A. man became more civilized
B. there was not a marketplace for farmers and smiths to exchange their goods
C. farmers hadn’t enough grain or meat to provide for skilled workers
D. more and more goods which had no fixed exchange values appeared on the market.
Money was not used until __________.
A. paper was invented
B. nothing could be offered in exchange
C. people practiced a simple process of exchange
D. the exchange of one thing for another became too complicated
What was used for trade according to the text?
A. Shells B. Tea C. Salt D. Horses
In the earliest stages of man’s development he had no more need of money than animals have. He was content with very simple forms of shelter, made his own rough tools and weapons and could provide food and clothing for himself and his family from natural materials around him. As he became more civilized, however, he began to want better shelter, more efficient tools and weapons, and more comfortable and more lasting clothing than could be provided by his own neighborhood or by the work of his own unskilled hands. For these things he had to turn to the skilled people such as smiths, leather workers or carpenters. It was then that the question of payment arose.
At first he got what he wanted by a simple process of exchange. The smith who had not the time to look after land or cattle was glad to take meat or grain from the farmer in exchange for an axe or a plough (犁). But as more and more goods which had no fixed exchange value came on the market, exchange became too complicated to be satisfactory. Another problem arose when those who made things wanted to get stocks of wood or leather, or iron, but had nothing to offer in exchange until their finished goods were ready.
Thus the difficulties of exchange led by degree to the invention of money. In some countries easily handled things like seeds or shells were given a certain value and farmer, instead of paying the smith for a new axe by giving him some meat or grain, gave him so many shells. If the smith had any shells left when he had bought his food, he could get stocks of the raw materials of his trade. In some countries quite large things such as cows or camels or even big flat stones were used for trade. Later, pieces of metal, bearing values according to the rarity (稀有) of the metal and the size of the pieces, or coins were used. Money as we know it had arrived.
What does the first paragraph mainly tell us?
A. Man needed little in the earliest stages of development.
B. Man preferred to make tools by himself.
C. How the simple process of exchange arose.
D. What the early man needed from others.
As men became more civilized they __________.
A. all learnt to make by themselves the things needed
B. had to travel a lot to look for what they wanted
C. wanted better things than those they themselves could provide
D. no longer provided food and clothing for themselves
Exchange of goods became difficult because __________.
A. man became more civilized
B. there was not a marketplace for farmers and smiths to exchange their goods
C. farmers hadn’t enough grain or meat to provide for skilled workers
D. more and more goods which had no fixed exchange values appeared on the market.
Money was not used until __________.
A. paper was invented
B. nothing could be offered in exchange
C. people practiced a simple process of exchange
D. the exchange of one thing for another became too complicated
What was used for trade according to the text?
A. Shells B. Tea C. Salt D. Horses
完形填空:
阅读下面短文,掌握其大意,然后从1~25各题所给的四个选项中,选出一个最佳答案.
The cold afternoon sunlight made long shadows behind the trees along the road. Sam Higbee 1 the gate of the Higbee Place and 2 his tractor (拖拉机) into the field.
Things had been moving 3 . Only the night before, the Higbee 4 had at last stopped quarrelling for long enough to agree on a 5 price. John Farnham, the real-estate agent (房地产代理商), had 6 a hurried trip to see Higbee the next morning. Within a few hours Higbee had looked round the place again, the agreement had been 7 , and he had put his horses into one of the Higbee fields. Now he was 8 to plough (犁地). He'd work until midnight, or 9 if the didn't get too 10 .
Out in the center of the field the old house was 11 the big trees. A dusty road ran 12 the field to the house from the gate. 13 Higbee had no use for the big old house. The 14 would cost more than the place was 15 .
He lowered the 16 and started the tractor. 17 he ploughed the rich black earth 18 out in smooth furrows (犁沟). Low dark clouds moved past overhead, and in the west the 19 sun turned the lower parts of the clouds red.
The 20 of the tractor's motor was unchanging, and watching the furrows sent Sam into a dream-like 21 He didn't notice the time 22 . When it got dark, he 23 the headlight and kept going. The 24 night air caused sharp pain to his face and hands, but his 25 remained fixed on the piece of ground between the grass and the ploughed earth.
1. A. looked at |
B. opened |
C. pushed |
D. knocked at |
[ ] |
2. A. drove |
B. moved |
C. carried |
D. rode |
[ ] |
3. A. sometimes |
B. carelessly |
C. slowly |
D. quickly |
[ ] |
4. A. house |
B. home |
C. family |
D. place |
[ ] |
5. A. selling |
B. buying |
C. rising |
D. different |
[ ] |
6. A. made |
B. tried |
C. planned |
D. delayed |
[ ] |
7. A. missing |
B. read |
C. seen |
D. singed |
[ ] |
8. A. stopping |
B. starting |
C. continuing |
D. forced |
[ ] |
9. A. harder |
B. shorter |
C. longer |
D. earlier |
[ ] |
10. A. sleepy |
B. hungry |
C. excited |
D. sad |
[ ] |
11. A. between |
B. among |
C. in |
D. under |
[ ] |
12. A. over |
B. into |
C. through |
D. below |
[ ] |
13. A. Therefore |
B. Or |
C. And |
D. But |
[ ] |
14. A. repairs |
B. buildings |
C. painting |
D. checks |
[ ] |
15. A. useful |
B. worth |
C. sold |
D. bought |
[ ] |
16. A. machine |
B. wheels |
C. head |
D. plough |
[ ] |
17. A. For |
B. Since |
C. As |
D. Because |
[ ] |
18. A. rolled |
B. ran |
C. walked |
D. went |
[ ] |
|
19. A. shining |
B. strong |
C. setting |
D. falled |
[ ] |
|
20. A. voice |
B. sound |
C. size |
D. movement |
[ ] |
|
21. A. place |
B. situation |
C. form |
D. state |
[ ] |
|
22. A. turning |
B. moving |
C. passing |
D. disappearing |
[ ] |
|
23. A. turned on |
B. turned off |
C. opened |
D. fixed |
[ ] |
|
24. A. warm |
B. cold |
C. hot |
D. dirty |
[ ] |
|
25. A. thought |
B. face |
C. hands |
D. eyes |
[ ] |
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com