
3.一般将来时的常用结构
①用于“I expect, I'm sure, I think, I wonder + 宾语从句”中
Don't worry about the exam. I'm sure you'll pass.
不要担心这次考试,我确信你会通过的。
I wonder what will happen.
我不知道将会发生什么事。
I don't think the test will be very difficult.
我想这次测验不会太难。
②用于“祈使句 + and + 陈述句”中
Work hard and you will succeed.
如果你努力,就会成功的。
Go at once and you will see her.
马上去,你就会见到她了。
③与表示时间或条件的状语从句连用
I'll let you know as soon as he arrives.
他一到我就通知你。
If you ask him, he will help you.
如果你请他,他会帮助你的。
We shall go unless it rains.
除非下雨,否则我们是要去的。
2.一般将来时的用法
①表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态
I shall be free this afternoon.
我今天下午有空。
There'll be no chemistry classes tomorrow.
明天没有化学课。
They will probably go to Shanghai for their holiday.
他们可能去上海度假。
注意:
在口语中,常用will / shall + be doing结构来代替will / shall + 动词原形,以表示生动。
I'll be seeing a friend off at the airport.
我要去机场给一个朋友送行。
He'll be going with us tomorrow.
他明天和我们一起去。
②表示将要反复发生的动作
My uncle will come to see me every Saturday.
我叔叔每个星期六都会来看我。
The students will have five English classes per week this term.
本学期学生们每周要上五节英语课。
③表示同意或答应做某事
That bag looks heavy. I'll help you with it.
这个包看起来很重,我来帮你提。
I won't tell anyone what happened, I promise.
我保证不告诉别人所发生的事。
④表示一种倾向或推测
Flowers will die without water.
没有水花会枯死的。
Water will change into ice at 0℃.
水在零摄氏度就会结冰。
This will be your sister, I guess.
我猜想这是你姐姐。
1. 一般将来时的构成
一般将来时是由“will / shall + 动词原形”构成的。shall只限于第一人称,主要见于英国英语,现在的趋势是第一、二、三人称的单复数形式均用will表示。在口语中,shall和will常缩写成“'ll”,紧接在主语之后。其否定式shall not 和will not 常简略为shan't 和won't。
I'll go and shut the door.
我去关门。
When will you know your exam results?
你什么时候能知道考试结果?
I can see you're busy, so I won't stay long.
我看得出你很忙,所以我不会呆太久的。
提示:在you and I或both of us等短语后,只用will,不用shall。
You and I will arrive there next Monday.
我和你下周一都要到达那里。
Both of us will graduate from middle school next year.
我们俩明年中学毕业。
3.一般现在时和一般过去时的比较
一般现在时要和现在时间相联系,而一般过去时和说话的“现在”不相联系。
His father is a film director.
他父亲是电影导演。(他现在还是)
His father was a film director.
他父亲曾是电影导演。(他现在不是)
How do you like the novel?
你觉得这部小说怎么样?(还在看小说)
How did you like the novel?
你觉得这部小说怎么样?(已看完小说)
C.一般将来时
1. 一般过去时的构成
一般过去时是用动词的过去式来表示。
His words fetched a laugh from all present.
他的话使在场的人都笑了。
I did not sleep well last night.
我昨晚没睡好。
Did you direct the tourist to the hotel?
你告诉这位游客去旅馆的路了吗?
2.一般现在时的用法
①一般现在时的基本用法
a. 表示现在习惯性的动作或存在状态
He always takes a walk after supper.
晚饭后他总是散散步。
Everyone is in high spirits now.
现在大家都情绪高涨。
b. 表示客观事实或普遍真理
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
太阳从东方升起在西方落下。
Sound travels faster through water than it does through air.
声音在水中的传播速度要比在空气中快。
Time and tide wait for no man.
时间不等人。
c. 表示主语的特征、能力和状态
This cloth feels soft.
这布摸上去很软。
I love classical music.
我喜欢古典音乐。
The President still seems able to find time to go fishing.
看来总统仍能有时间去钓鱼。
d. 表示按计划或安排将要发生的动作
The meeting begins at 7:00.
会议七点钟开始。
We leave here at 8:00 sharp.
我们八点整离开这里。
e. 在时间、条件、让步状语从句中表示将来动作
When you come next time, bring me some magazines.
你下次来时,给我带几本杂志。
If time allows, we shall go there tomorrow.
如果时间允许的话,我们明天去那里。
Whether he agrees or not, I will stay at home.
不管他同意与否,我都会待在家里。
②一般现在时的特殊用法
a. 用于新闻标题或图片说明中
China Declares Manned Spaceflight Successful
中国宣布载人航天飞行圆满成功
Laura Bush Arrives in Moscow
劳拉·布什抵达莫斯科
b. 用于体育运动、表演等实况报道中
Francis slips past, passes the ball to Yao Ming, who jumps, catches and shoots it into the basket.
弗朗西斯穿过去,把球传给姚明,姚明跳起来,接住球投进篮里。
Now, look, I press the button and turn on the machine.
现在,看,我按下按扭,打开了这台机器。
c. 表示告诫或劝说
You mind your own business.
你不要管闲事!
If he does that again, he goes to prison.
如果他再那样的话,他就会进监狱的。
d. 表示现在瞬间的动作
Here comes the bus.
汽车来了。
There goes the bell.
铃响了。
B.一般过去时
一般时包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和一般过去将来时。
A.一般现在时
1. 一般现在时的构成
一般现在时主要用动词原形来表示。主语是第三人称单数时,动词后面要加-s或-es。
They want good jobs.
他们想要好的工作。
The coat matches the dress.
外衣和裙子很相配。
This work does not satisfy me.
这项工作我不满意。
Do you understand?
你懂了吗?
20.(本小题满分14分)已知数列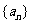 的前
的前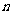 项和为
项和为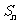 ,点
,点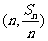 在直线
在直线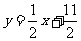 上;数列
上;数列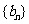 满足
满足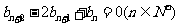 ,且
,且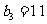 ,它的前9项和为153.
,它的前9项和为153.
(1)求数列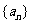 、
、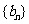 的通项公式;
的通项公式;
(2)设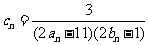 ,数列
,数列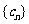 的前
的前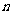 项和为
项和为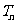 ,求使不等式
,求使不等式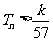 对一切
对一切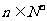 都成立的最大正整数
都成立的最大正整数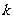 的值;
的值;
(3)设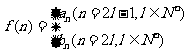 ,是否存在
,是否存在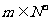 ,使得
,使得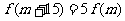 成立?若存在,求出
成立?若存在,求出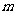 的值;若不存在,请说明理由.
的值;若不存在,请说明理由.
19.(本小题满分14分)某工厂生产甲、乙两种产品,已知生产每吨甲、乙两种产品所需煤、电力、劳动力、获得利润及每天资源限额(量大供应量)如下表所示:
 产品 产品消耗量 资源 |
甲产品(每吨) |
乙产品(每吨) |
资源限额(每天) |
|
煤(t) |
9 |
4 |
360 |
|
电力(kw·h) |
4 |
5 |
200 |
|
劳动力(个) |
3 |
10 |
300 |
|
利润(万元) |
6 |
12 |
|
问:每天生产甲、乙两种产品各多少吨,获得利润总额最大?
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com