
8.某单位要邀请10位教师中的6人参加一个研讨会,其中甲、乙两位教师不能同时参加,则邀请的不同方法有
A.84种 B.98种 C.112种 D.140种
7.函数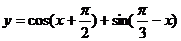 具有性质
具有性质
A.最大值为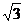 ,图象关于直线
,图象关于直线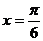 对称
对称
B.最大值为1,图象关于直线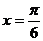 对称
对称
C.最大值为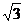 ,图象关于
,图象关于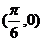 对称
对称
D.最大值为1,图象关于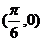 对称
对称
4.已知函数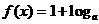
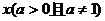 ,
,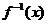 是
是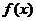 的反函数,若
的反函数,若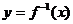 的图象过点
的图象过点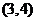 ,则
,则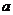 等于
等于
A.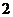 B.
B.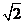 C.
C.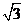 D.
D.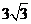
5.已知两个非零向量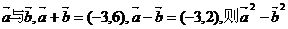 的值为
的值为
A.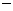 3 B.
3 B.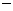 24 C.21 D.12
24 C.21 D.12
6.经过抛物线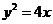 的焦点,且方向向量为
的焦点,且方向向量为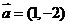 的直线
的直线 的方程是
的方程是
A.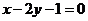 B.
B.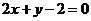
C.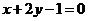 D.
D.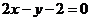
3.等差数列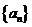 中,
中,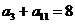 ,数列
,数列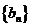 是等比数列,且
是等比数列,且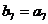 ,则b6b8的值为
,则b6b8的值为
A.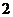 B.
B.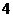 C.
C.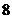 D.
D.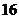
2.若集合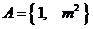 ,集合
,集合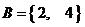 ,则“
,则“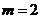 ”是“
”是“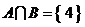 ”的
”的
A.充分不必要条件 B.必要不充分条件
C.充分必要条件 D.既不充分也不必要条件
只有一项是符合题目要求的.)
1.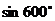 的值是
的值是
A.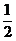 B.
B.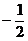 C.
C.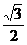 D.
D.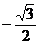
7. Do with Part C2 on page 96 in Workbook. (It can be assigned as homework.)
|
Answers: 1. has she 2. didn’t they 3. are there 4. hasn’t he 5. does she 6. won’t they 7. did they 8. could he 9. shall we 10. will you |
5. 相关链接:
(1)一般情况下, 当陈述句部分是主从复合句时,简略问句的主语和谓语动词与主句的主语和谓语动词一致。
(2)当陈述句部分属于否定前移情况时,简略问句的主语和谓语与从句的主谓语一致,而且要把否定考虑在内。
(3)对“否定陈述句+ 肯定句”回答时,注意其形式和汉语意译。
-He doesn’t like talking too much , does he? -Yes, he does. (不,他喜欢。)
-No, he doesn’t. (是的,他不喜欢。)
-I don’t believe you are serious in your studies, are you? –Yes, I am.(不,我认真。)
–No, I am not. (是的,我不认真。)
(4)祈使句加简略问句,表示请求。常为以下几种情况:
肯定/否定祈使句+ will you ?
Let us …, will you?
Let’s …, shall we?
Let me…, shall I ?
6. Now let’s deal with Parts A and B in Question tags on page 51.
|
高考试题赏析(2002上海) Mrs. Black doesn’t believe her son is able to design a digital camera, _____? A. is she B. isn’t she C. doesn’t she D. does she 解析:该题考查反意疑问句,按照前否后肯的原则,应是does she。答案:D |
|
Answers: A. (1) don’t you (2) isn’t he (3) does he (4) doesn’t she (5) aren’t they (6) can you (7) don’t they (8) can’t you B. (2) You have completely recovered, haven’t you? (3) You thought you were going to die, didn’t you? (4) You never thought you would be saved by a stranger in China, did you? (5) It’s dangerous to take weight-loss pills, isn’t it? (6) There is nothing more important than good health, is there? |
4. 反意疑问句
反意疑问句是疑问句的一种,基本结构是“陈述句+简略问句”。(1)肯定陈述句+ 否定问句 (2) 否定陈述句+ 肯定问句
注意:陈述句中含有否定词never, no , none, nobody, no one, nothing, few, little(几乎没有),seldom, barely, scarcely等时, 简略问句用肯定形式。陈述句中只是有带否定前缀(im- , un-, il-, dis-)或后缀(-less)的词时,简略问句仍用否定形式。e.g.:
You still go to the gym every day, don’t you?
She has been to the Great Wall three times, hasn’t she?
Nobody has heard from his, have they?
Neither of them can speak French, can they?
Seldom does he have lunch at school, does he?
He’s unable to finish his homework on his own, isn’t he?
Your father dislike noisy music , doesn’t he?
3.Generally speaking, after negative statements, the ordinary interrogative is used, while after affirmative statements, the negative interrogative is used. And we use auxiliary verbs, modal verbs or be in their proper forms to form a question tag. For example,
You didn’t see him at the party, did you?
Ann was there, wasn’t she?
Mary can’t swim, can she?
Peter often helps the old man, doesn’t he?
Note: I’m late, aren’t I?
When the main clause of the sentence begins with I think/ suppose/ guess and is followed by an object clause introduced by that, the question tag is like this:
I think everyone will be interested in these after school activities, won’t they?
I guess they haven’t heard about our plan, have they?
I don’t think John went back home early last night, did he?
Note the question tag in sentences with ’s or ’d. For example,
You’d watch the football match rather than go to the party, wouldn’t you?
He’d written to you before you phoned, hadn’t he?
He’s a very good teacher, isn’t he?
She’s been in hospital for two weeks, hasn’t she?
湖北省互联网违法和不良信息举报平台 | 网上有害信息举报专区 | 电信诈骗举报专区 | 涉历史虚无主义有害信息举报专区 | 涉企侵权举报专区
违法和不良信息举报电话:027-86699610 举报邮箱:58377363@163.com